In its long 119-year journey, Harley-Davidson has continuously upgraded the engine. They have worked with the engine design, increased its power and displacement capacity, and introduced newer technologies for these engines.
As a result, each upgrade has seen brilliant engineering. The iron head and shovelhead engines are no exception. Harley Davidson brought these two engines during the 1950s to improve their motorcycle performance. These two engines share many similarities. Thus, people are keen to compare Ironhead vs Shovelhead Engine for Harley motorcycles. Likewise, they share almost identical technology and engineering.
Here, We will go through their similarity and dissimilarity. Also, we will see which engine is comparatively better. So, Harley Davidson lovers, let’s see the shovelhead and ironhead engine discussion.
What Is Ironhead Engine?
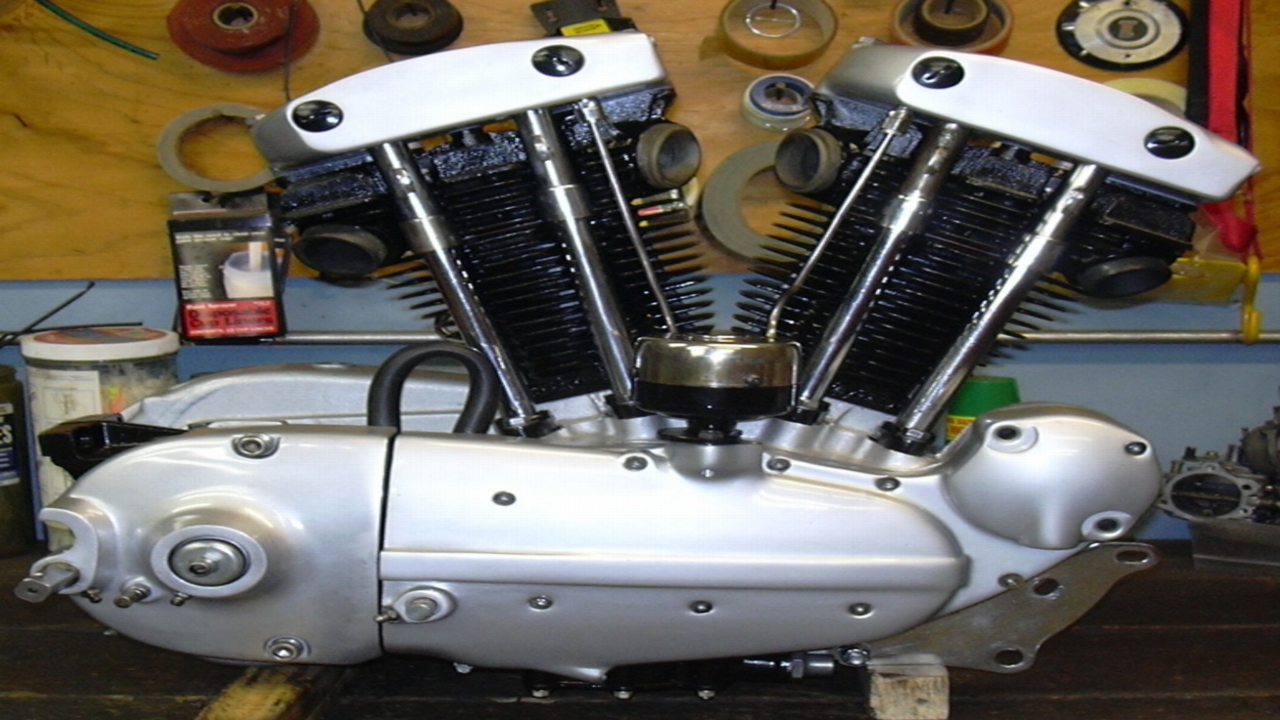

Harley introduced the excellent ironhead engine in 1957. They discontinued the engine in 1985 when their Evo Engine came. So, it got its name from the materials handy in its cylinder gearhead. Yes, this engine has irons instead of aluminum in the cylinder shovel head.
It immediately got its name when Harley integrated the engine with their motorcycles. This engine was made for the compact yet powerful Sportster versions. It was a two-cylinder engine. Plus, each cylinder had two valves. The engine got three major upgrades during its stay in the market for almost 28 years. With each upgrade, we improved the engine’s specifications.
What Is A Shovelhead Engine?
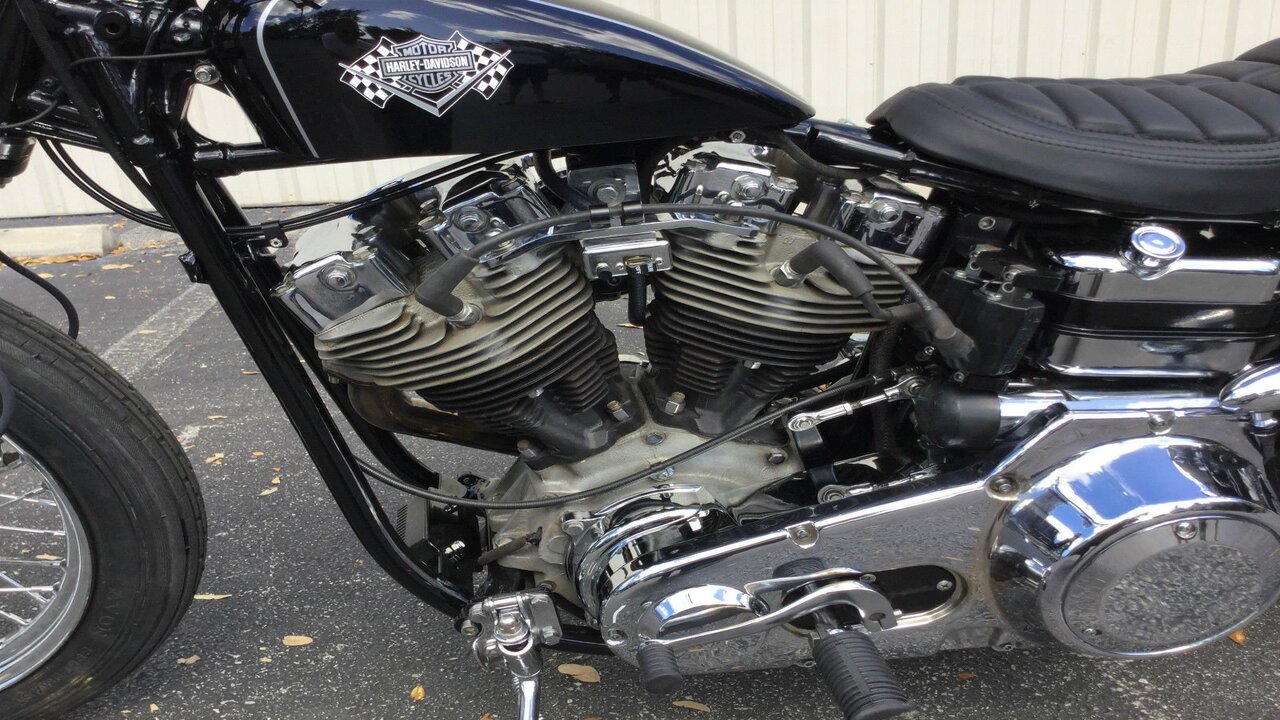

A Shovelhead engine is a type of V-twin engine that was manufactured by Harley-Davidson from 1966 to 1984. This iconic engine was named after the distinctive shape of its rocker box covers, which resembled the shape of a shovel. The Shovelhead engine is highly regarded in the motorcycle community for its unique design and historical significance.
The Shovelhead engine was a significant advancement for Harley-Davidson, as it introduced several improvements over its predecessor, the Panhead engine. One notable feature of the Shovelhead engine is its increased power and performance. With its larger displacement and improved combustion chamber design, the Shovelhead engine offered riders a smoother and more powerful riding experience.
Ironhead Vs Shovelhead Engine Comparison

The Ironhead and Shovelhead are iconic options with distinct characteristics regarding Harley-Davidson engines. The Ironhead engine, produced from 1957 to 1985, is known for its sleek appearance and compact design.
It features overhead valves and a single camshaft, which gives it a distinctive sound and plenty of torque. On the other hand, the Shovelhead engine, produced from 1966 to 1984, is named for its shovel-shaped rocker covers. This engine has a larger displacement than the Ironhead and offers improved performance and reliability. Scroll down to get details on Ironhead Vs Shovelhead Engine.
Ironhead And Shovelhead Engine Specifications Comparison
Here is an informative table comparing the specifications of Ironhead and Shovelhead engines:
|
Specification |
Ironhead Engine |
Shovelhead Engine |
|
Engine Type |
V-twin engines |
V-Twin |
|
Displacement |
883cc or 1000cc |
1200cc |
|
Bore and Stroke |
3.000″ x 3.812″ |
3.498″ x 4.250″ |
|
Compression Ratio |
9:1 |
7.2:1 |
|
Horsepower |
50-60 HP |
60-70 HP |
|
Torque |
50-55 lb-ft |
70-75 lb-ft |
|
Valve Configuration |
Overhead Valves (OHV) |
Overhead Valves (OHV) |
|
Ignition System |
Points |
Electronic |
|
Fuel System |
Carburetor |
Carburetor |
|
Cooling System |
Air-cooled |
Air-cooled |
|
Production Years |
1957-1985 |
1966-1984 |
Please note that these specifications may vary depending on the specific model and modifications made to the engines.
Engine Design And Configuration Comparison
The Ironhead and Shovelhead engines are two iconic engine designs in motorcycles. The Ironhead engine, produced by Harley-Davidson from 1957 to 1985, is popular for its distinctive overhead valve configuration and iron cylinder iron heads. On the other hand, the Shovelhead engine, produced from 1966 to 1984, features a unique shovel-shaped rocker box cover and aluminum cylinder heads.
While both engines have unique characteristics and loyal fan bases, they also have some key differences in performance and maintenance. The Ironhead engine is often praised for its durability and simplicity, while the Shovelhead engine is popular for its smooth power delivery and classic aesthetic.
Displacement And Compression Ratio Comparison
When comparing the Ironhead and Shovelhead engines, one important factor is the displacement and compression ratio. The Ironhead engine typically has a smaller displacement compared to the Shovelhead engine, which can affect its overall power and performance. On the other hand, the Shovelhead engine is popular for its larger displacement and higher compression ratio, which can result in increased torque and horsepower.
Ultimately, the choice between these two modern engines will depend on your specific needs and preferences and the riding you plan to do. It is recommended to consult with an experienced mechanic or Harley-Davidson enthusiast to determine which engine option would be best suited for your motorcycle.
Valve Train And Camshaft Configuration Comparison
When comparing the Ironhead and Shovelhead engines, one key factor is the valve train and camshaft configuration. The Ironhead engine features a single camshaft in the crankcase, which operates both the intake and exhaust valves.
This configuration allows for efficient operation and easy maintenance. On the other hand, the Shovelhead engine utilizes a separate camshaft for each cylinder, which can provide more precise control over valve timing and lift. However, this design can be more complex and require frequent maintenance.
Cooling System Comparison Comparison
One important aspect to consider when comparing the Ironhead and Shovelhead engines is their cooling systems. The Ironhead engine features air cooling, which relies on natural airflow to dissipate heat. This can be effective for shorter rides or cooler climates but may result in overheating during extended periods of use or hotter temperatures.
On the other hand, the Shovelhead engine introduced a more advanced cooling system known as oil-cooling. This system uses oil passages to transfer heat away from critical engine components, improving cooling efficiency and overall performance. The oil-cooling system of the Shovelhead engine makes it a popular choice among riders who value reliability and durability.
Horsepower And Torque Output Comparison

When comparing the Ironhead and Shovelhead engines, one of the key factors to consider is their horsepower and torque output. The Ironhead engine, produced from 1957 to 1985, typically had lower horsepower and torque than its counterpart, the Shovelhead engine. From 1966 to 1984, the Shovelhead engine gained a reputation for increased power and performance.
With advancements in technology and design, the Shovelhead engine delivered higher horsepower and torque levels, making it a popular choice among motorcycle enthusiasts. However, it’s important to note that the horsepower and torque output can vary depending on various factors, such as modifications or upgrades to the engine block.
Acceleration And Top Speed Capabilities Comparison
Regarding comparing the acceleration and top speed capabilities of the Ironhead and Shovelhead engines, there are a few key factors to consider. The Ironhead engine, known for its durability and reliability, offers solid acceleration and decent top speeds.
On the other hand, the Shovelhead engine, with its larger displacement and more advanced design, tends to provide smoother acceleration and higher top speeds.
However, it’s important to note that the actual performance of these engines can vary depending on various factors such as modifications, maintenance, and overall bike builder setup. Choosing an Ironhead or Shovelhead engine ultimately depends on your preferences and riding style.
Fuel Efficiency Comparison
When comparing the fuel efficiency of Ironhead and Shovelhead engines, it is important to consider several factors. The Shovelhead engine introduced several improvements that increased fuel efficiency, including a larger combustion chamber and improved intake and exhaust flow.
While both engines have unique characteristics and appeal to different riders, those looking for better fuel efficiency may lean towards the Shovelhead engine. It is always recommended to consult with a knowledgeable mechanic or do thorough research before making any decisions about motorcycle engines.
Longevity And Lifespan Of The Engines Comparison
When comparing the longevity and lifespan of Ironhead and Shovelhead engines, it is important to consider several factors. The Ironhead engine, produced by Harley-Davidson from 1957 to 1985, is known for its durability and longevity. With proper maintenance and care, an Ironhead engine can last for many years.
On the other hand, the Shovelhead engine, which was produced from 1966 to 1985, has a reputation for being less reliable than the Ironhead. This is due in part to design flaws and manufacturing issues that were present in some Shovelhead engines.
However, with proper maintenance and periodic rebuilds, a Shovelhead engine can still have a decent lifespan. With the qualifications of an Expert, the kit bike program manager conducted a thorough comparison of the longevity and lifespan of the engines.
Overall Reliability And Performance Under Different Conditions Comparison

When comparing the Ironhead and Shovelhead engines, it is important to consider their overall reliability and performance under different conditions. The Ironhead engine, produced from 1957 to 1985, is popular for its durability and ability to handle high compression ratios.
It is a solid choice for riders who value low-end torque and prefer a more aggressive riding style. On the other hand, the Shovelhead engine, produced from 1966 to 1984, offers a smoother ride and improved cooling capabilities. It is a popular choice among riders who prioritize comfort and long-distance touring.
Advantages Of Ironhead Engine
The Ironhead engine, known for its durability and reliability, has several advantages, making it a popular choice among motorcycle enthusiasts. One of the main advantages of the Ironhead engine is its simplicity. With fewer moving parts than other engines, such as the Shovelhead, it is easier to maintain and repair.
This can save both time and money in the long run. The Ironhead engine is also known for its torque and power, making it a great option for riders who enjoy a more aggressive riding style. Its compact size also allows for better maneuverability on the road. Overall, the Ironhead engine offers a reliable and powerful performance many riders appreciate.
Disadvantages Of Ironhead Engine
While the Ironhead engine has advantages, it also has some disadvantages. One of the main drawbacks of the Ironhead engine is its reputation for reliability issues. Due to its design and construction, it has been known to require more frequent maintenance and repairs compared to other engine types.
Additionally, the Ironhead engine can be more difficult to work on and find replacement parts for, as it is an older model that is no longer in production. This can make repairs more time-consuming and costly. Another disadvantage of the Ironhead engine is its lower power output than newer engine designs. It may not provide the same level of performance or acceleration as other engines on the market.
Advantages Of Shovelhead Engine
In addition to the specific advantages of the Ironhead and Shovelhead engines, there are a few other factors to consider when deciding. One important aspect is the availability of aftermarket parts and accessories. While both engines may require some searching, finding replacement parts for the Ironhead engine can be more challenging due to its older design and discontinued production.
Disadvantages Of Shovelhead Engine
While the Shovelhead engine has its merits, there are also some disadvantages. One of the main drawbacks is its reputation for being less reliable and more prone to mechanical issues than other Harley-Davidson engines.
The Shovelhead’s design, with its separate rocker boxes and pushrod tubes, can lead to oil leaks and gasket failures. Finding replacement parts for the Shovelhead can be more challenging than finding newer engines, resulting in higher repair costs. Despite these disadvantages, many enthusiasts still appreciate the vintage charm and unique sound of the Shovelhead engine.
Conclusion
There are several factors to consider when choosing between an Ironhead vs Shovelhead Engine. Both engines have their unique characteristics and appeal to different types of riders. The Ironhead engine is known for its simplicity and reliability, making it a popular choice for those who prefer a classic and low-maintenance ride.
On the other hand, the Shovelhead engine offers more power and performance, making it suitable for riders who crave speed and a bit of extra horsepower. Ultimately, deciding between these iconic engines will depend on your preferences and riding style. Whichever engine you choose, both the Ironhead and Shovelhead offer a thrilling and nostalgic experience on the road.
FAQs
Is An Ironhead The Same As A Shovelhead?
No, an ironhead and a shovelhead are not the same. They are both types of Harley-Davidson motorcycle engines, but they have different designs and features. The ironhead refers to the Harley-Davidson Sportster engine produced from 1957 to 1985, known for its iron cylinder heads.
Why Is It Called An Ironhead?
“Iron head” refers to a specific type of Harley-Davidson motorcycle engine shaft produced from 1957 to 1985. It earned this nickname due to its distinctive cast iron cylinder aluminum heads, known for their durability and strength.
Are Shovelhead Engines Reliable?
Shovelhead engines have a reputation for being reliable, but they require regular maintenance and attention to ensure their longevity. Proper care and handling, including regular oil changes, valve adjustments, and keeping the engine properly cooled, can greatly enhance their reliability.
What Engine Replaced The Shovelhead?
The Evolution, the Evo, replaced the Shovelhead in Harley-Davidson motorcycles. Introduced in 1984, the Evolution engine marked a significant advancement in Harley-Davidson’s engine technology.
Which Harley Has The Biggest Engine?
The Harley-Davidson CVO Road Glide Ultra is the motorcycle with the biggest engine in the Harley lineup. It is equipped with a massive 117 cubic inch (1923cc) Milwaukee-Eight engine, providing unparalleled power and performance on the road.

Shovelheads were 74” and 80” not 75” so you lost most guys not being right there-
My bought new 77 XLCH has over 200,000 miles on it
Original generator
Clutch lasted 190,000
Transmission 195,000
Batteries 7 years
Tires 12-15000
Never left me on the side of the road
2 up (280 lbs) with 24 tooth front sprocket at 55 mph (1979) 65 mpg on I-26 from Columbia to Charleston
Only oil leak was a crack in the oil tank vent tube where it was brazed in
Would never trade for a shovel….